UNIT 2: HARDWARE AND ITS COMPONETS.
In this unit you will find out the answer to the questions:
- How do you use a computer to find, process, organise, presen and sotre information.
- What are the basic componets of a personal computer? How are the used and connected?. What is their function in a computer?
- What are the basic operations performed by an operating system?
LINK UNIT2: Hardware_and_Componets.
TASK 1
1. Daily life can be affected by ICT systems.
A Listening to the radio
B Doing the ironing
C Feeding your pet
D Watching TV
Put a cross in one box to show which aspect of daily life would not be affected
immediately by the failure of an associated ICT system.
A -_
B - X
C - X
D -_
2. Describe the similarities and differences between data and information.
This is the raw information to be processed – just like the raw food
Data is the raw information to be processed – just like the raw food, and information is data that people understand. In order to understand data.
3. Explain what is meant by hardware.
is the equipment that makes up the physical ICT system. That is, the keyboard, the monitor screen, the system unit and everything inside it, and other devices connected to it, such as a printer.
4. Draw a labelled diagram of a desktop computer system showing the range of
hardware devices that could be attached to it.
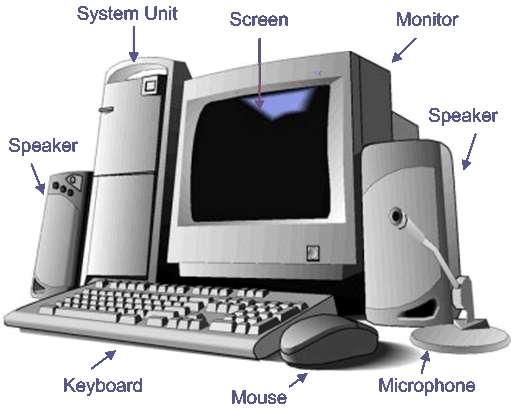
5. Describe the similarities and differences between a desktop computer and a
laptop computer.
A laptop is a computer which is designed to be portable. Usually this entails making sacrifices in terms of performance and utility. Laptops are intended for people who travel a lot and need a computer which can go with them.
A desktop computer is meant to be stationary. This usually results in a lower price and better options for upgrading. Desktops are intended for permanent workstations and generally have more power and storage capacity than laptops.
A desktop computer also know as a tower computer is the cheaper more customizable option if the two that can offer significantly better performance at a cheaper cost yet is not portable at all. A laptop is an all-in-one machine that is very portable, runs off a battery. Both can be upgraded but the laptop is easy to upgrade in RAM and hard drive space only.
6. Describe the similarities and differences between a desktop computer and a
hand-held computer.
Hand-held computers are more expensive--there are other distinctions between hand-held computers and PDA devices. A personal digital assistant usually requires a stylus pen for operation although foldable and wireless PDA keyboards are available. Hand-held computers are somewhat larger than PDAs and newer models come with a built-in keyboard. Functionally speaking, there is no substantive difference between a hand-held computer and a PDA.
7. Explain how a PDA user can benefit from having an external keyboard.
Although PDAs can be temporarily attached to a keyboard, you cannot comfortably type a long document into a PDA. The keyboard can help to the user to write faster and to have beter movility and adaptation
8. Figure 1.2 shows the flow of data through the input–output process. If the input
was the intake of pupils into a school, describe what would represent the
‘PROCESS’, the ‘INSTRUCTIONS’ and the ‘FINAL OUTPUT’ (see Figure 1.8).
Process- teorical class, different materials.
Instrucition- steps, activities, stunding.
Final output- knowledge.
Task 2
1. Find out what type of motherboard you have installed on your computer. Locate the BIOS ROM chip on a motherboard. What make of BIOS ROM is it?
Gigabyte Technology Co., Ltd. GA-MA69VM-S2 x.x
BIOS ID: 03/03/2008-RS690V-SB600-6A669G01C-00
System Model: GA-MA69VM-S2
BIOS Version: F8
• The BIOS boots up the PC, i.e. it starts up the PC every time it is turned on.
• The BIOS checks the actual hardware configuration against the configuration data.
• The BIOS handles the input and output of the computer, allowing the operating system to use particular features of hardware within the configuration.
2. Identify the main components on a motherboard. Draw a diagram to show the position of the processor chip, the BIOS chip, the battery, the power supply connector, the memory slots, the expansion slots, the ports and other important components. Look at how components are slotted into place.

3. Turn on your computer and watch the POST process. Note what happens if one part of your system is not working or has been
disconnected (such as a LAN cable).
The computer gives problems and beeps.
Task 4
1.Locate the processor on a motherboard. What cooling device is used?
A heat sink. In electronic systems, a heat sink is a passive component that cools a device by dissipating heat into the surrounding air.Heat sinks are used to cool electronic components such as high-power semiconductor devices, and optoelectronic devices such as higher-power lasers and light emitting diodes.
2.Research the Internet for data on heat sinks. What materials might these be made from?
Are usually made of aluminum for light weight, but also copper, better heat conductor. Weight is important as the technology advances and therefore lighter sinks are required and sufficient for the efficient transfer of heat to the outside.
3.Research the Internet to find out what happens (and at what temperature) if the fan stops working on a PC, or the heat sink is removed or not connected properly to the processor chip.
The computer is running much slower and fails, and the motherboard temperature increases may even burn.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y39D4529FM4
Task 5
1 What types of internal memory are being used in your computer? How much is installed?
Internal memory is used for two main purposes: to store programs that are being run and to store the data that the program works on. Programs that are written and stored in RAM are called software – the instructions can be overwritten. To preserve data and/or program
instructions for use later, these have to be stored either on ROM or to a secondary storage device such as a hard disk RAM memory chips provide a form of memory that offers the same access time for allocations within it
RAM and ROM memory. My PC have 1.83 GB of memory RAM
Nonvolatile BIOS memory refers to a small memory on PC motherboards that is used to store BIOS settings. It was traditionally called CMOS RAM because it used a volatile, low-power complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) SRAM (such as the Motorola MC146818 or similar) powered by a small battery when system power was off.
A CPU cache is a cache used by the central processing unit of a computer to reduce the average time to access memory. The cache is a smaller, faster memory which stores copies of the data from the most frequently used main memory locations. As long as most memory accesses are cached memory locations, the average latency of memory accesses will be closer to the cache latency than to the latency of main memory.
2 Research the Internet to find out how much cache memory is used in a number of PCs with different specifications.
The cache is structured, a 512 KiB L2 cache is divided into 16,384 rows and 63 columns named Tag RAM, which tells how much of the RAM is associated each cache line, ie translate an address in RAM particular cache line.
LINK : ICT_1
1.1. WHAT IS COMPUTER SCIENCE?.
Computer science is the techniques and knoledge necessary to automatically process information using a computer.
A computer works like a system that collects INPUT data, processes it (organises, saves and transforms) and transmit into OUTPUT information.
ACTIVITY Nº1.
a) Make a summary in your blog about this concept.
Explain how it works using a drawing (input/process/output).
Input: you press the keyboard, and the computer sends information to the control unit
Processes it: Control Unit, process the information that you send to Pc
Output: Information, etc
Feedback: My shelf, checking if it works properly
1.2. BINARY CODE. What is a byte?
Computers use binary code.
The "brain" of a computer (microprocessor) has millions of tiny switches that are activated and desactivated automatically. When a switch is open, the microprocessor interprets this as a "0" and when it´s closed as a "1". Each of these digits, either 0 or 1, is called a bit (digit binary) and a group of 8bits is called a Byte.
And example of a binary code is ASCII. It is used to represent all the characters used on computers. Each symbol or letter is encoded by a group of 8 bits.
The value of the binary numbering systems depends on their position in the group (like in decimal numberin), in this case the value is determined by a base-2 system.
* To convert a binary number into a decimal number we foinf the successive powers of 2, starting with 2^0, followed by 2^1, etc.
Example: 1011=1*2^3+0*2^2+1*2^1+1*2^0= 8 + 0 + 2 + 1 + 0 = 11
* To convert a decimal number into a binary number we divide the decimal number by 2 successively until the quotient is 1. Then you put the remainders of the quotients in order from right to left.
Example: (25/2=12 remainder=1); (12/2=6 remainder=0); (6/2=3 remainder=0); (3/2=1 remainder=1); therefore: 25 = 11001
ACTIVITY Nº2.
a) Make a table with the multiples of a byte.
1 Byte
|
8 Bits
|
1 Kilobyte
|
1024 Bytes
|
1 Megabyte
|
1024 Kilobytes
|
1 Gigabyte
|
1024 Megabytes
|
1 Terabyte
|
1024 Gigabytes
|
1 Petabyte
|
1024 Terabytes
|
1 Exabyte
|
1024 Petabytes
|
b) How many bytes are there in 5KB, 8MB, and 10GB.
5 KB = 5120 Bytes
8 MB = 8388608 Bytes
10 GB = 10737418240 Bytes
c) Look at the order ASCII code uses to represent the first six letters of the alphabet.
A = 01000001
B= 01000010
C= 01000011
D= 01000100
E= 01000101
F= 01000110
d) Convert the decimal number 27 into binay number.
27 = 11011
e) Convert the binary number 11101 into a decimal number.
11101 = 29
f) Convert the decimal number 255 into binary number.
255= 11111111
g) Convert these units: 2^10KB= 1MB.
1048576 mega bytes
1.3. COMPUTER COMPONETS: HARWARE.
Hardware are the physical componets of the computer, such as internal circuits, the wiring, monitor, keyboard, printer, etc.
(LINK YOUTUBE: "Disecting PC")
CPU.
MEMORIES: RAM and ROM.
STORY DEVICES: magnetic, optical solid state.
PERIPHERAL DEVICES: input, output or input/output.
ACTIVITY Nº3
a) Make a picture explaning the hardware of a computer.

b) Find out how a chip is made of.
A computer chip is any small electronic device that contains an integrated circuit (IC). What that means is if you look at an ordinary electronic circuit, like the copper lines on the green boards in a radio, that circuit gets miniturized and integrated into a ‘chip’
c) Find out what kind of CPU is working nowdays. List two of them with theirs features.
The big hype today in the computer tech world is the quad core CPU. It is advertised with speed of 2.4 or 2.66GHZ.
d) Find out how many types of RAM memory are?
SDRAM (Synchronous DRAM)
Almost all systems used to ship with 3.3 volt, 168-pin SDRAM DIMMs
SDRAM (Synchronous DRAM)
Almost all systems used to ship with 3.3 volt, 168-pin SDRAM DIMMs.
Rambus DRAM (RDRAM)
Despite it's higher price, Intel has given RDRAM it's blessing for the consumer market, and it will be the sole choice of memory for Intel's Pentium 4.
DIMMs vs. RIMMs
DRAM comes in two major form factors: DIMMs and RIMMS.
e) Make a table where you can compare the capacities of the differents storage devices.
Flash drivers,- 1,000 GB
External Harde devices.- 2TB
Smart cards.-
f) Find out the types of monitors are. Drescribe it.
CRT Monitors.- Cathode Ray Tube, or in simpler words CRT, are oldest among all available models these days. These monitors function on the old cathode ray tube phenomena.
LCD Monitors.- liquid crystal display monitors are not the latest but the later version than CRT monitors. Unlike CRT monitors, these monitors are compact and slim.
Plasma Monitors.- Plasma screen and/or plasma monitors are considered as high contrast screen with bright, vibrant colors and brightness that claims to make your visual experience worthwhile.
SED Monitors.- SED is abbreviated form of Surface-conducted electron-emitted display. These are high resolution and flat penal display screens. Some of these display units are even more than 40 inches in diagonal measurements.
Other Monitors.- Other than, all mentioned types of monitors there are Digital Light Processing Monitors, these monitors are also known as projectors and digital projectors. It works on Digital Light processing phenomena.
g) Make a set of slides about a componet and upload it using www.slideshare.net . In this case you have to look for information into the file that you can link over here:ICT2_HARDWARE
QRCODE
QR Codeis the trademark for a type of matrix barcode (or two-dimensional code) first designed for the automotive industry. More recently, the system has become popular outside the industry due to its fast readability and large storage capacity compared to standard UPC barcodes. The code consists of black modules (square dots) arranged in a square pattern on a white background. The information encoded can be made up of four standardized kinds ("modes") of data (numeric, alphanumeric, byte/binary, Kanji), or through supported extensions, virtually any kind of data.
ACTIVITY Nº4:
a) WORK_SHOP
b) CROSS_WORD
c) QUIZ
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario